React源码学习进阶(六)completeWork究竟做了什么
源码解析
function performUnitOfWork(unitOfWork: Fiber): Fiber | null {
// 这里没有子节点了,走completeUnitOfWork
if (next === null) {
// If this doesn't spawn new work, complete the current work.
next = completeUnitOfWork(unitOfWork);
}
ReactCurrentOwner.current = null;
return next;
}function completeUnitOfWork(unitOfWork: Fiber): Fiber | null {
// Attempt to complete the current unit of work, then move to the next
// sibling. If there are no more siblings, return to the parent fiber.
workInProgress = unitOfWork;
do {
// The current, flushed, state of this fiber is the alternate. Ideally
// nothing should rely on this, but relying on it here means that we don't
// need an additional field on the work in progress.
const current = workInProgress.alternate;
const returnFiber = workInProgress.return;
// Check if the work completed or if something threw.
if ((workInProgress.effectTag & Incomplete) === NoEffect) {
setCurrentDebugFiberInDEV(workInProgress);
let next;
if (
!enableProfilerTimer ||
(workInProgress.mode & ProfileMode) === NoMode
) {
next = completeWork(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime);
} else {
startProfilerTimer(workInProgress);
next = completeWork(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime);
// Update render duration assuming we didn't error.
stopProfilerTimerIfRunningAndRecordDelta(workInProgress, false);
}
stopWorkTimer(workInProgress);
resetCurrentDebugFiberInDEV();
resetChildExpirationTime(workInProgress);
if (next !== null) {
// Completing this fiber spawned new work. Work on that next.
return next;
}
if (
returnFiber !== null &&
// Do not append effects to parents if a sibling failed to complete
(returnFiber.effectTag & Incomplete) === NoEffect
) {
// Append all the effects of the subtree and this fiber onto the effect
// list of the parent. The completion order of the children affects the
// side-effect order.
if (returnFiber.firstEffect === null) {
returnFiber.firstEffect = workInProgress.firstEffect;
}
if (workInProgress.lastEffect !== null) {
if (returnFiber.lastEffect !== null) {
returnFiber.lastEffect.nextEffect = workInProgress.firstEffect;
}
returnFiber.lastEffect = workInProgress.lastEffect;
}
// If this fiber had side-effects, we append it AFTER the children's
// side-effects. We can perform certain side-effects earlier if needed,
// by doing multiple passes over the effect list. We don't want to
// schedule our own side-effect on our own list because if end up
// reusing children we'll schedule this effect onto itself since we're
// at the end.
const effectTag = workInProgress.effectTag;
// Skip both NoWork and PerformedWork tags when creating the effect
// list. PerformedWork effect is read by React DevTools but shouldn't be
// committed.
if (effectTag > PerformedWork) {
if (returnFiber.lastEffect !== null) {
returnFiber.lastEffect.nextEffect = workInProgress;
} else {
returnFiber.firstEffect = workInProgress;
}
returnFiber.lastEffect = workInProgress;
}
}
} else {
// This fiber did not complete because something threw. Pop values off
// the stack without entering the complete phase. If this is a boundary,
// capture values if possible.
const next = unwindWork(workInProgress, renderExpirationTime);
// Because this fiber did not complete, don't reset its expiration time.
if (
enableProfilerTimer &&
(workInProgress.mode & ProfileMode) !== NoMode
) {
// Record the render duration for the fiber that errored.
stopProfilerTimerIfRunningAndRecordDelta(workInProgress, false);
// Include the time spent working on failed children before continuing.
let actualDuration = workInProgress.actualDuration;
let child = workInProgress.child;
while (child !== null) {
actualDuration += child.actualDuration;
child = child.sibling;
}
workInProgress.actualDuration = actualDuration;
}
if (next !== null) {
// If completing this work spawned new work, do that next. We'll come
// back here again.
// Since we're restarting, remove anything that is not a host effect
// from the effect tag.
// TODO: The name stopFailedWorkTimer is misleading because Suspense
// also captures and restarts.
stopFailedWorkTimer(workInProgress);
next.effectTag &= HostEffectMask;
return next;
}
stopWorkTimer(workInProgress);
if (returnFiber !== null) {
// Mark the parent fiber as incomplete and clear its effect list.
returnFiber.firstEffect = returnFiber.lastEffect = null;
returnFiber.effectTag |= Incomplete;
}
}
const siblingFiber = workInProgress.sibling;
if (siblingFiber !== null) {
// If there is more work to do in this returnFiber, do that next.
return siblingFiber;
}
// Otherwise, return to the parent
workInProgress = returnFiber;
} while (workInProgress !== null);
// We've reached the root.
if (workInProgressRootExitStatus === RootIncomplete) {
workInProgressRootExitStatus = RootCompleted;
}
return null;
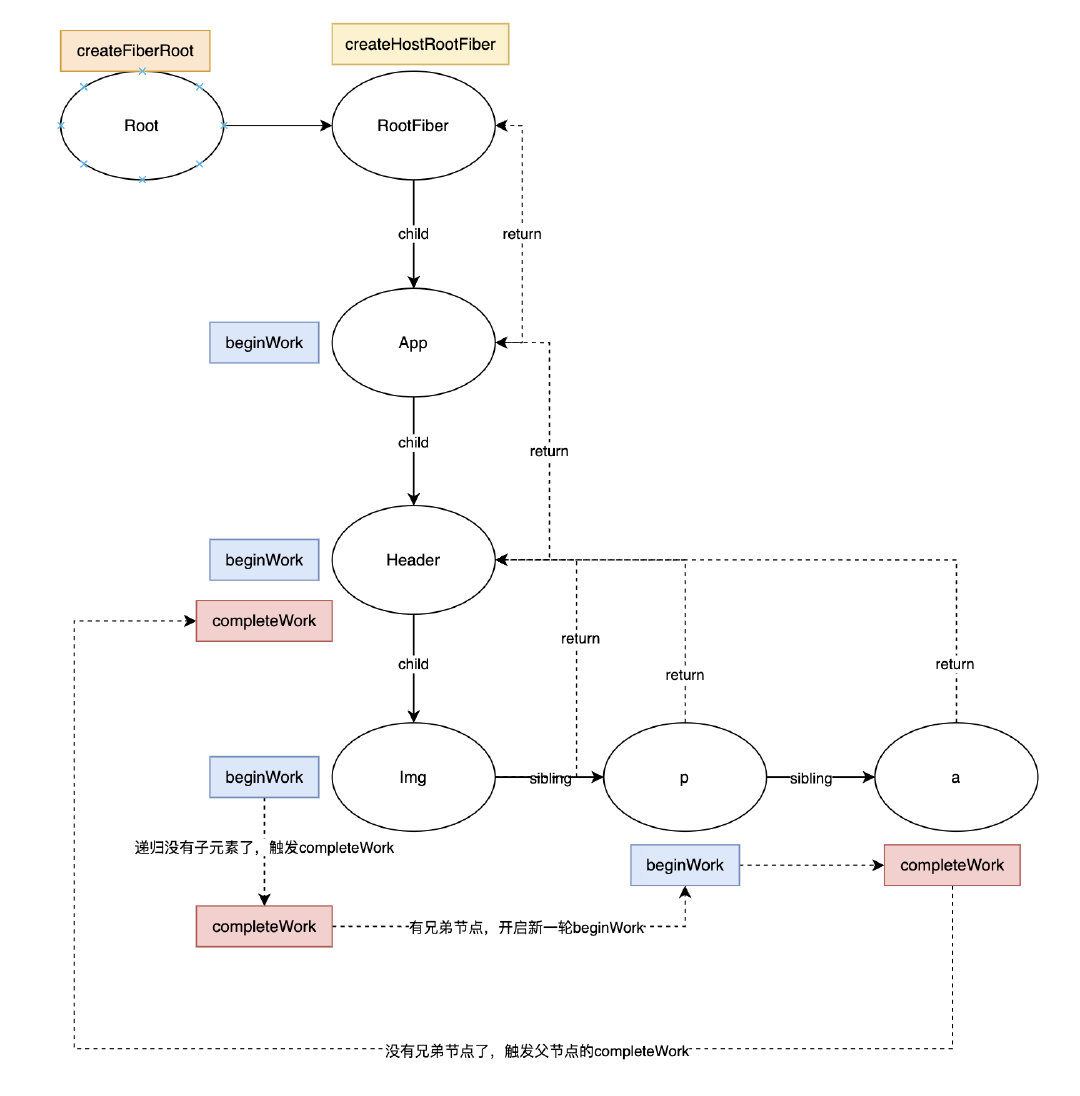
}小结一下
Last updated